In the world of 3D printing, the success of your model largely depends on selecting the right type of filament. Whether you’re creating a detailed STL figure or a functional part, understanding the properties of different 3D printer filaments is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore various filament types suitable for crafting with 3D model STL, STL figure, figure STL, and other 3D printer files. We’ll also discuss how each filament can affect the quality and functionality of your 3D print STL and craft machine files.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Filament Types
- PLA Filament: The Best for 3D Model STL
- ABS Filament: Durable and Versatile
- PETG Filament: Impact Resistance for 3D STL File
- TPU Filament: Flexibility for Your STL Figure
- Specialty Filaments: Enhancing Your Figure STL
- Choosing the Right Filament for Your 3D Printer File
Introduction to Filament Types
When selecting your 3D Printer Filament Types for your 3D printer files, consider the properties that are most important for your project, such as strength, flexibility, and the level of detail it can hold. Each type of filament offers different advantages and limitations, which can significantly affect the outcome of your 3D print STL or figure STL.
PLA Filament: The Best for 3D Model STL

Polylactic Acid (PLA) is one of the most popular filaments due to its ease of use and environmental friendliness. It’s derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. PLA is particularly suitable for crafting detailed 3D model STL and 3D printer files because it offers a fine level of detail and a smooth finish.
- Advantages: Easy to print with, requiring lower temperatures. Does not warp easily, making it ideal for large 3D print STL projects.
- Disadvantages: Less durable and more brittle compared to other filaments, which might not be ideal for mechanical parts.
ABS Filament: Durable and Versatile
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is known for its toughness and impact resistance, making it a great choice for durable parts from 3D STL file or craft machine files. It’s widely used in professional applications that require high durability.
- Advantages: High durability, resistance to high temperatures, and slightly flexible.
- Disadvantages: Requires higher temperatures to print and can emit unpleasant odors during printing.
PETG Filament: Impact Resistance for 3D STL File
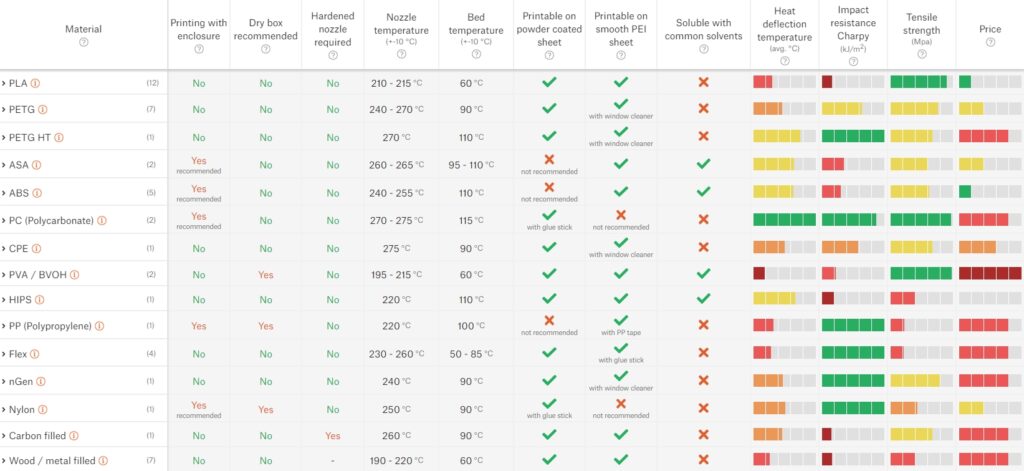
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) combines the ease of PLA with the strength of ABS. It is impact-resistant and provides excellent flexibility, which is perfect for 3D STL file applications where toughness is required.
- Advantages: No odors during printing, high impact resistance, and very durable.
- Disadvantages: Can be sticky during printing and may require fine-tuning of print settings.
TPU Filament: Flexibility for Your STL Figure
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a flexible filament that is ideal for printing bendable and stretchable parts. This makes TPU perfect for STL figure that require movement or flexibility.
- Advantages: Highly flexible and durable; good for parts that undergo strain.
- Disadvantages: Can be challenging to print due to its flexibility; requires slow printing speeds.
Specialty Filaments: Enhancing Your Figure STL
There are numerous specialty filaments that can add unique properties to your 3D printer files, such as wood-like, metal-filled, or glow-in-the-dark filaments. These are great for adding a special touch to your figure STL or other 3D model STL.
Choosing the Right Filament for Your 3D Printer File
Selecting the right filament for your 3D printer files depends on the specific requirements of your project. Consider the mechanical properties, aesthetic qualities, and post-processing needs of your 3D print STL or craft machine files before making a decision.
Understanding these various types of filaments will help you optimize your 3D printer files and achieve the best results for your 3D model STL, STL figure, figure STL

